InnoDB is a general-purpose storage engine that balances high
reliability and high performance. In MySQL 8.0, InnoDB is the default
MySQL storage engine. Unless you have configured a different default
storage engine, issuing a CREATE TABLE statement without an ENGINE
clause creates an InnoDB table.
InnoDB是一种平衡高可靠性和高性能的通用存储引擎。在MySQL
8.0中,InnoDB是MySQL默认的存储引擎。除非您配置了不同的默认存储引擎,否则发出不带
ENGINE 子句的 CREATE TABLE 语句将创建一个 InnoDB 表。
Read More
GROUP_CONCAT()函数输出的结果,发现被截取了一部分,并没有显示完整,原来GROUP_CONCAT()
默认的输出长度为1024字节,超出的部分会被截掉不显示。
Read More
1. SpringBoot
1.1 SpringBoot的作用
SpringBoot是一个快速构建项目并简化项目配置的工具,内部集成了Tomcat及大多数第三方应用和Spring框架的默认配置。与我们学习的SpringMVC和SpringCloud并无冲突,SpringBoot提供的这些默认配置,大大简化了SpringMVC、SpringCloud等基于Spring的Web应用的开发。
1.2.SpringBoot的自动配置原理(如何实现)?
SpringBoot的自动配置是如何实现的?
一般我们的SpringBoot项目启动类都会添加@SpringBootApplication注解,而这个注解的其中一个二级注解是@EnableAutoConfiguration注解。而@EnableAutoConfiguration注解通过@Import注解,以ImportSelector接口的方法来导入classpath下的META-INF/spring.factories文件,这些文件中会指定需要加载的一些类名称。
这些类一般都加了@Configuration注解,并且完成了对某框架(例如Redis、SpringMVC)的默认配置,当这些类符合条件时,就会被实例化,其中的配置生效,那么自动配置自然生效了。
Read More
执行update更新操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <update id ="batchUpdate" parameterType ="java.util.List" > <foreach collection ="list" item ="item" separator =";" open ="" close ="" > update test_table <set > <if test ="item.a != null" > output_amount = #{item.a},</if > <if test ="item.b!= null" > invoice_amount = #{item.b},</if > <if test ="item.c!= null" > payment_amount = #{item.c},</if > </set > where id = #{item.id} </foreach > </update >
执行报错: 1 2 3 4 Error updating database. Cause: java.sql.SQLSyntaxErrorException: You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near 'update test_table set a = 1, ' at line 14
刚开始出现这个错误,以为是update语句写的有问题,但是检查了很多遍都没有问题。奇怪的是,同样的代码,同样的数据,本地启的环境不行,测试环境却可以。经过同事提醒了一下,于是检查了一下配置文件,果然发现配置文件上的jdbc配置,测试环境比开发环境多了个allowMultiQueries=true。
1 jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/db?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&allowMultiQueries=true&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&nullCatalogMeansCurrent=true
MyBatis默认情况下不允许批量插入或更新数据的原因是出于安全考虑。在许多情况下,数据的插入和更新都需要经过验证和控制,以确保数据的完整性和一致性。如果允许默认的批量操作,可能会导致不正确的数据插入或更新,从而影响应用程序的正常运行。
通过配置allowMultiQueries=true可以开启MyBatis的批量操作功能。这个配置项告诉MyBatis允许在单个数据库连接中执行多个SQL语句,从而实现批量插入或更新数据的功能。但是要注意,在开启批量操作之前,确保你已经了解并理解了可能引发的安全风险,并且在使用批量操作时要进行适当的验证和控制,以确保数据的完整性和安全性。
Read More
使用HistoryService接口来查询历史流程实例
在Flowable中,已终止的流程实例不能通过RuntimeService接口直接查询到。相反,你需要使用HistoryService接口来查询历史流程实例,并从中筛选出已终止的实例。以下是正确的步骤:
确保你的应用程序连接到正确的Flowable流程引擎实例。你需要使用Flowable的API来执行后续的操作。
使用HistoryService接口的createHistoricProcessInstanceQuery()方法构建查询,设置适当的条件来筛选已终止的流程实例。
1 2 HistoricProcessInstanceQuery query = historyService.createHistoricProcessInstanceQuery() .finished();
执行查询并获取已终止的流程实例列表。
1 List<HistoricProcessInstance> terminatedInstances = query.list();
根据需要选择要重启的流程实例。你可以根据流程实例的ID或其他属性进行选择。
如果你需要将已终止的流程实例重新激活,可以创建一个新的流程实例,或者使用历史流程实例中的数据进行修复。请注意,这取决于你的业务需求和流程定义的复杂性。
请注意,已终止的流程实例是历史数据,因此无法直接重新激活。你需要根据业务需求进行相应的处理。使用HistoryService接口可以提供有关已终止流程实例的详细信息,但不能直接操作它们。
Read More
1 2 List<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); Long[] item = list.toArray(new Long [0 ]);
List<String>直接以toArray的方式转换Long数组是错误的,运行后报错:
1 Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayStoreException
查看java.util.List.toArray(T[])方法,注释中明确写到:
@throws
ArrayStoreException if the runtime type of the specified array is not a
supertype of the runtime type of every element in this list
如果指定数组的运行时类型不是此列表中每个元素的运行时类型的超类型
明显Long类型不是String类型的超类。
可以通过下面的方式实现
1 2 List<String> stringList = Arrays.asList("1" , "2" , "3" ); Long[] item = list.stream().map(Long::valueOf).toArray(Long[]::new );
Read More
背景描述:SpringBoot项目构建打包生成的jar包,在资源文件夹下有个普通txt文件,路径:/templates/content.txt
方式一:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 File file = new File (ResourceUtils.getURL("classpath:" ).getPath());File templateFile = new File (file, "/templates/content.txt" );BufferedReader reader = null ;StringBuffer sbf = new StringBuffer ();try { reader = new BufferedReader (new FileReader (file)); String tempStr; while ((tempStr = reader.readLine()) != null ) { sbf.append(tempStr); } reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (reader != null ) { try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } } } return sbf.toString();
Read More
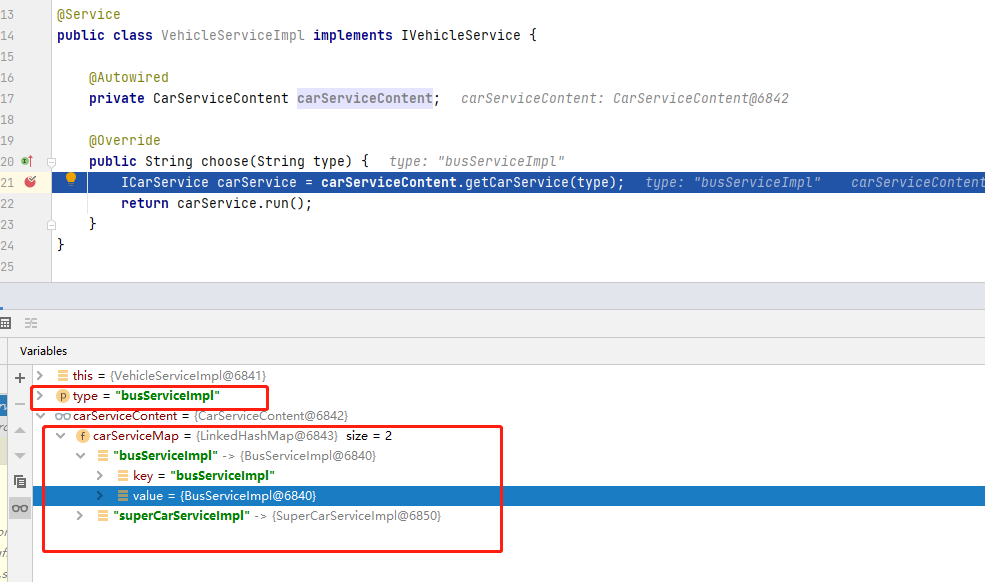
示例结构(红框内的)
工厂模式(Factory Pattern)是 Java
中最常用的设计模式之一。这种类型的设计模式属于创建型模式,它提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式。在工厂模式中,我们在创建对象时不会对客户端暴露创建逻辑,并且是通过使用一个共同的接口来指向新创建的对象。
作为一种创建类模式,在任何需要生成复杂对象的地方,都可以使用工厂方法模式。有一点需要注意的地方就是复杂对象适合使用工厂模式,而简单对象,特别是只需要通过
new
就可以完成创建的对象,无需使用工厂模式。如果使用工厂模式,就需要引入一个工厂类,会增加系统的复杂度。
Read More
单点登录 (SSO)
是一种身份验证过程,在该过程中,用户仅使用一组登录凭据即可访问多个应用程序或网站,这避免了用户分别登录不同应用程序需要输入不同验证信息的麻烦。用户凭据和其他识别信息由称为身份提供者(IdP)的集中式系统存储和管理。身份提供者是一个受信任的系统,可以提供对其他网站和应用程序的访问。基于单点登录
(SSO)
的身份验证系统通常用于员工需要访问其组织的多个应用程序的企业环境中。
Read More